3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from digital models. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block, 3D printing builds the final object by adding material layer by layer. This layer-by-layer approach can produce highly complex shapes and structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods. 3D printing can utilize a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological materials such as living cells. At the same time 3D printing offers advantages such as rapid prototyping, customization, reduced material waste, and the ability to create complex designs with high precision. It is widely used in numerous industries including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, construction and consumer products for prototyping, tooling and end-use part production. Today this article will introduce 3D printing from their types and characteristics.
First one-Fused Deposition Modeling
1.FDM
Working principle:
Fused deposition modeling is one of the most well-known types of 3D printing. It works by pushing plastic filament through a heated nozzle. The molten plastic is then laid down layer by layer until the part is complete. There are many different 3D filament types available - from solid thermoplastics to flexible thermoplastic elastomers.
Features:
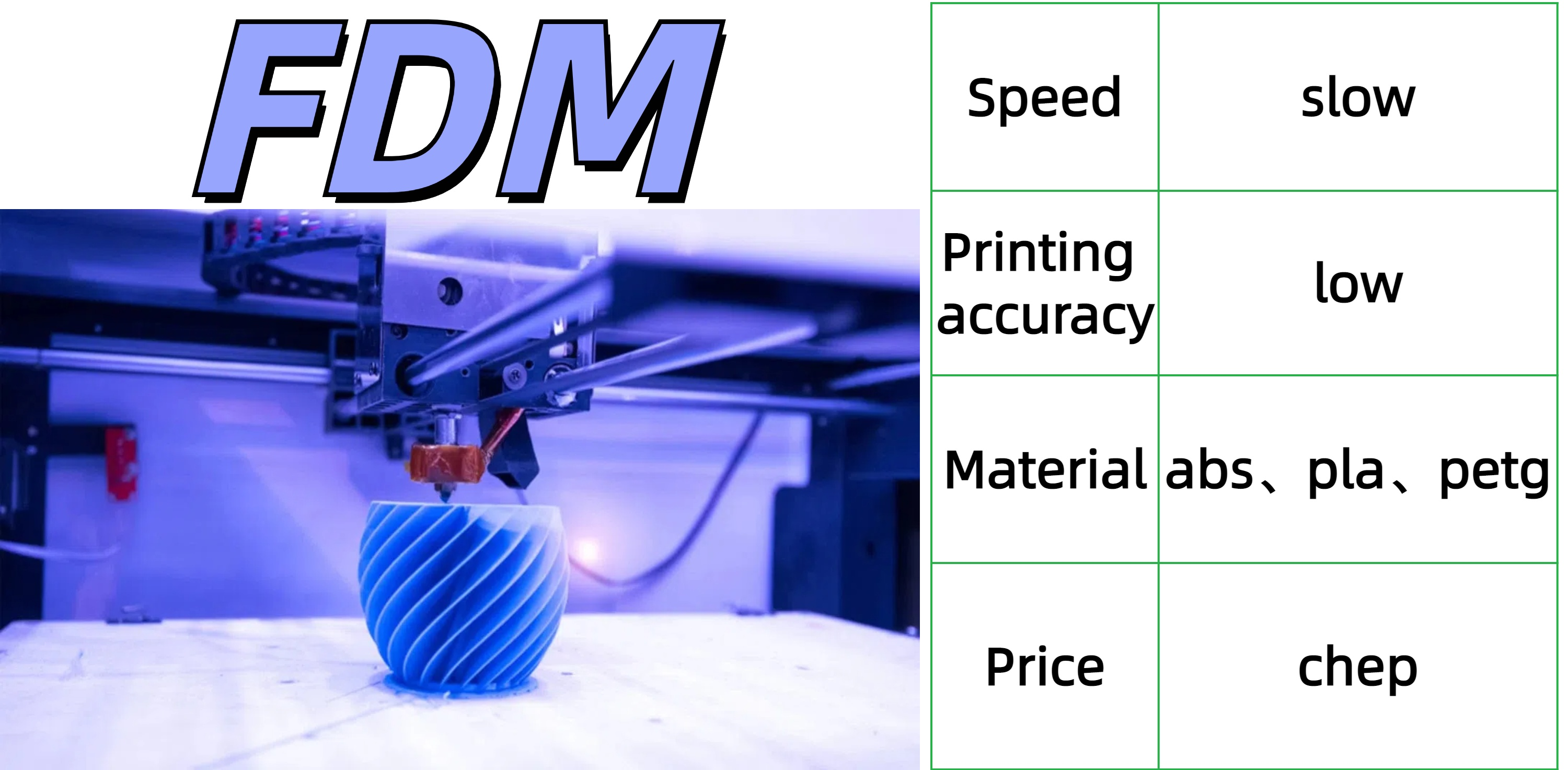
Disadvantage:
1. Printing speed is slow
2. The printed product has a thicker layer height
Second one-Light-Curing
1.SLA
Working principle:
Stereolithography was the first commercially available 3D printing technology. It works by solidifying a liquid photopolymer into the final part by tracing a high-power laser onto a build plate in the shape of the part's cross-section. The process continues as each subsequent layer aggregates onto the previous layer. This technology creates parts with extremely precise features.
Features:
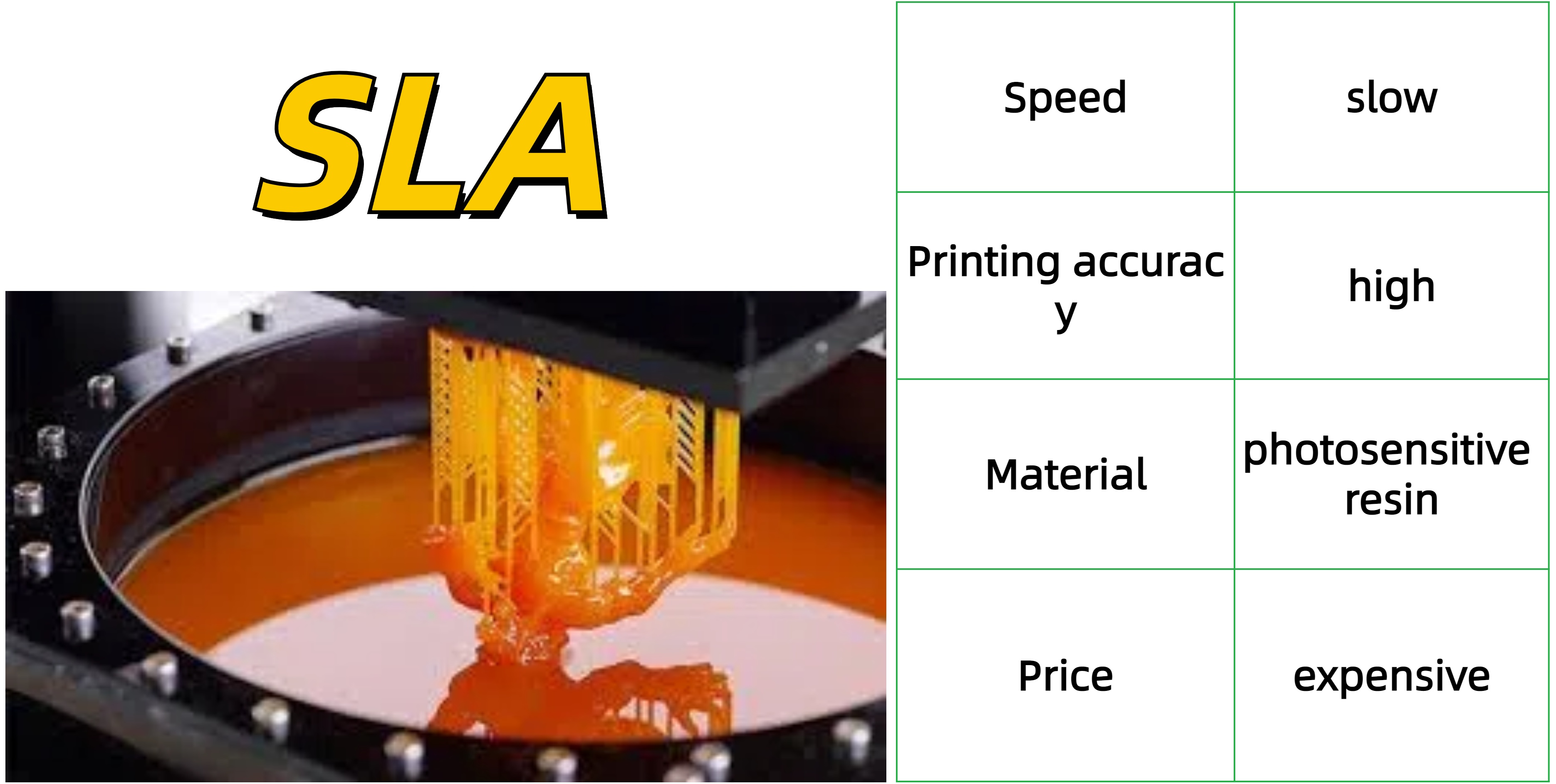
Disadvantage:
1. The material is irritating and slightly toxic
2. Expensive
3. After printing, clean, remove the bracket, and UV irradiation for secondary curing.
2.LCD
Working principle:
3D LCD printer is a printer that uses light-curing resin printing technology. Unlike traditional 3D printers that print layer by layer, LCD 3D printers use UV light to print entire layers at once. This means that 3D printing with a 3D LCD printer is faster and more precise than with other 3D printers.
What sets LCD 3D printers apart from other types of 3D printers, such as DLP or SLA printers, is their light source. LCD 3D printers use UV LCD arrays as light sources. Therefore, the light from the LCD panel hits the work area directly in a parallel manner. Because this light does not expand, pixel distortion is much less of an issue for LCD printing.
Features:
Disadvantage:
1. The LCD screen has a short life and needs to be replaced after printing for thousands of hours.
2. The material is irritating and slightly toxic.
Third one-Powder Fusion
SLS、SLM
Working principle:
Selective laser sintering works by placing a layer of powdered plastic and tracing the cross-section of the part with a laser. The laser melts the powder and fuses it. Another layer of plastic powder is laid on top of the previous layer, and the laser melts the cross-sectional shape while fusing it into the previous layer. If there are exit channels for unmelted powder, the process can produce high-precision parts that can be printed in place.
Features:

Disadvantage:
1. The cost is very expensive
2. Warping is prone to occur when printing large-size parts
3. There is a big smell when working
Summary
This article introduce the different 3D printing technology and feature according to types of 3D printing.To learn more about the 3D printing types and more about optimizing your 3D printed products, contact us.
Post time: May-29-2024
