In the design of plastic parts, the wall thickness of the part is the first parameter to be considered, the wall thickness of the part determines the mechanical properties of the part, the appearance of the part, the inject ability of the part and the cost of the part. It can be said that the selection and design of the wall thickness of the part determines the success or failure of the part design.
Part wall thickness must be moderate
Due to the characteristics of plastic materials and injection process, the wall thickness of plastic parts must be in a suitable range, not too thin, and not too thick.
If the wall thickness is too thin, the parts are injected when the flow of resistance, plastic melt is difficult to fill the entire cavity, have to be higher performance injection equipment to obtain higher filling speed and injection pressure.
If the wall thickness is too thick, parts cooling time increase (according to statistics, parts wall thickness increased by 1 times, cooling time increased by 4 times), parts molding cycle increases, parts production efficiency is low; at the same time, too thick wall thickness is easy to cause parts to produce shrinkage, porosity, warpage and other quality problems.
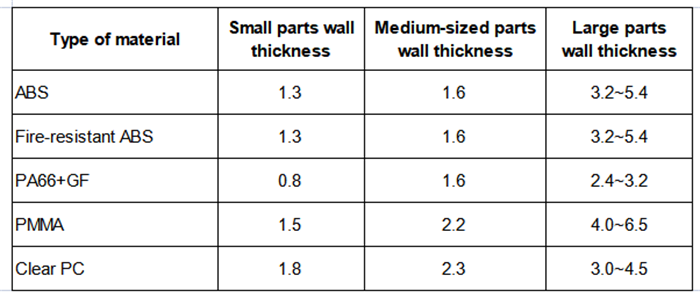
Different plastic materials have different requirements for the appropriate wall thickness of plastic parts, and even different plastic manufacturers of the same plastic material may also have different appropriate wall thickness requirements. Commonly used plastic material parts of the appropriate wall thickness range is shown in Table 1-1. When the wall thickness of plastic parts close to the upper and lower limits of the appropriate wall thickness value, the product design engineer should seek advice from the plastic manufacturer.
Table 1-1 Wall thickness selection for plastic parts
(unit:mm)
Key factors that determine the wall thickness of plastic parts:
1)Whether the structural strength of the part is sufficient. Generally speaking, the thicker the wall thickness, the better the strength of the part. But the wall thickness of the parts exceeds a certain range, due to shrinkage and porosity and other quality problems, increase the wall thickness of the parts will instead reduce the strength of the parts.
2) Can the part resist the ejection force when molding. If the part is too thin, it will be easily deformed by ejection.
3) Can ability to resist the tightening force during assembly.
4) When there are metal inserts, the strength around the insert is sufficient. General metal insert and the surrounding plastic material shrinkage is not uniform, easy to produce stress concentration, low strength.
5) The ability of parts to evenly disperse the impact forces to which they are subjected.
6) Whether the strength of the hole is sufficient, the strength of the hole is easily reduced because of the influence of fusion marks
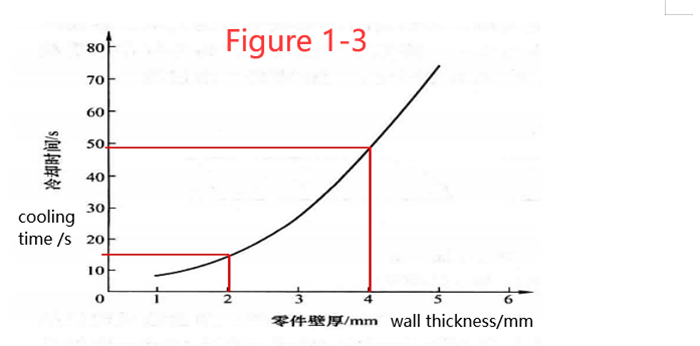
7) In the premise of meeting the above requirements, and injection molding will not produce quality problems,the wall thickness of plastic parts parts should be as small as possible, because a thicker part wall thickness will not only increase the material cost and weight of the part, but also extend the part molding cycle, thus increasing production costs. Figure 1-3 shows the relationship between wall thickness and cooling time for an ABS plastic part.
In order to ensure and improve part strength, product design engineers often tend to choose thicker part wall thicknesses.
In fact, it is not the best way to ensure and improve part strength by choosing a thicker part wall thickness. Part strength can be improved by adding reinforcement, designing curved or wavy part profiles, etc. This not only reduces the material waste of the part, but also shortens the injection molding cycle time of the part.
Uniform wall thickness of parts
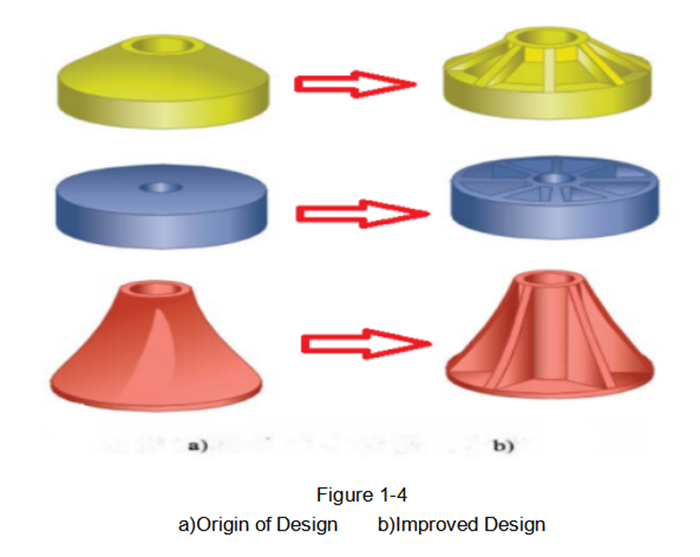
The most ideal wall thickness distribution of the parts is in any cross-section of the parts of uniform thickness. Uneven part wall thickness can cause uneven cooling and shrinkage of the part, resulting in surface shrinkage of the part, internal porosity, warpage and deformation of the part, dimensional accuracy is difficult to ensure defects.
Examples of common plastic parts with uniform wall thickness design are shown in Figure 1-4.
If the part uniform wall thickness is not possible to obtain, then at least need to ensure that the part wall thickness and thin wall at a smooth transition, to avoid sharp changes in the wall thickness of the part. Rapid changes in the wall thickness of the parts affect the flow of plastic melt, easy to produce stress marks on the back of the plastic, affecting the appearance of the product; at the same time easy to lead to stress concentration, reducing the strength of the plastic parts, making it difficult for the parts to withstand the load or external impact.
Four parts of the wall thickness of the uneven wall thickness design as shown in Figure 1-5.
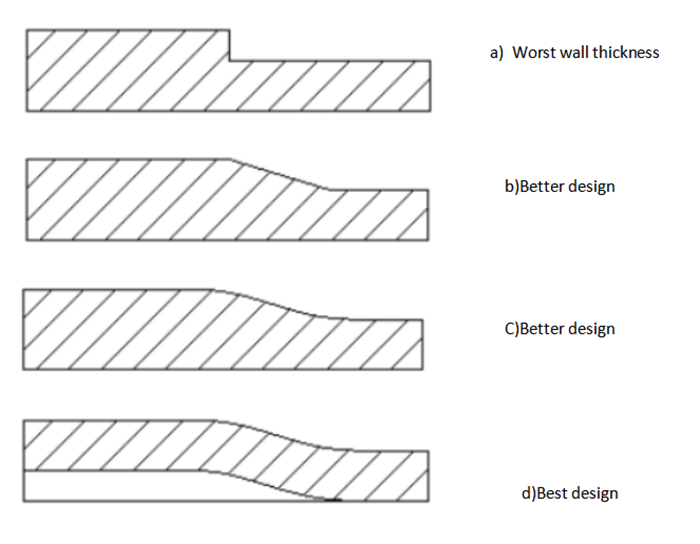
The worst wall thickness design is shown in a), where there is a sharp change in the wall thickness of the part;
Better wall thickness design is shown in Figure b) and c ), wall thickness at the thin wall uniform transition, in general, the length of the transition area is three times the thickness;
The best wall thickness design is shown in d), not only the part wall thickness smooth transition, but also in the part wall thickness using the hollow design, not only to ensure that the part does not shrink, but also to ensure the strength of the parts.
More Questions on the plastic parts wall thickness ,please feel free to contact us at admin@chinaruicheng.com .
The Latest Plastic Injection Molding Articles
NEED HELP?
Post time: Dec-22-2022
