ISO defines geometric tolerances as "Geometrical product specifications (GPS)−Geometrical tolerancing−Tolerancing of form, orientation, location and run-out". In other words, "geometrical characteristics" refers to the shape, size, positional relationship, etc. of an object, and "tolerance" is the "tolerance of error". The characteristic of "geometric tolerance" is that it not only defines the size, but also the tolerance of shape and position.
The difference between dimensional and geometric tolerances:
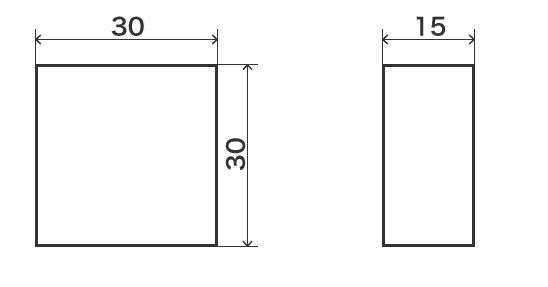
The methods of labeling design drawings can be broadly divided into two categories: "dimensional tolerances" and "geometric tolerances". Dimensional tolerances control the length of each part.
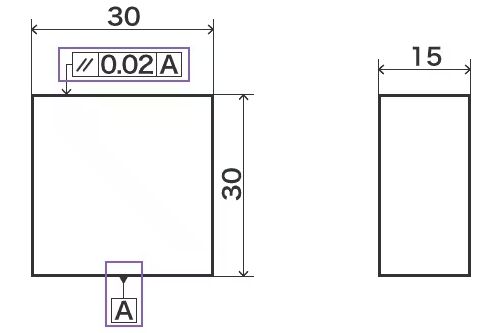
Geometric tolerances control shape, parallelism, inclination, position, runout, and so on.
Dimensional Tolerance Drawing
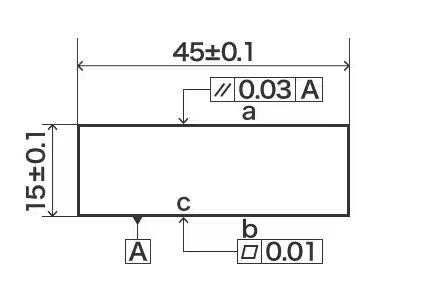
Geometric tolerance drawing
It means "ensure that surface A does not exceed a parallelism of 0.02".
Why should you mark geometric tolerances?
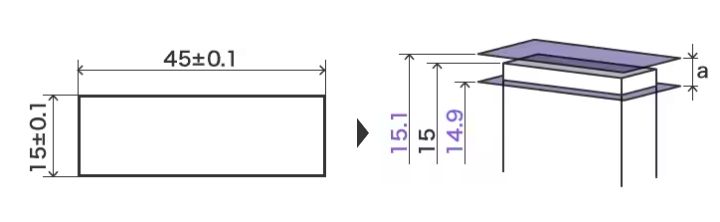
For instance, when ordering a plate part, the designer specified dimensional tolerance as below.
A Band of tolerance
However, according to the drawings above, the manufacturer can provide these parts.
A Band of tolerance
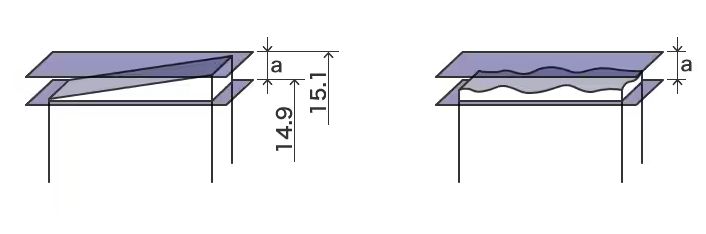
Parts may become unsuitable or defective if parallelism is not marked on the drawing.
The manufacturer is not responsible, but rather the designer's tolerance marking.Drawings of the same part marked with geometric toleration can result in the design shown below. Geometric tolerance information, such as "parallelism" and "planarity", is added to the figure based on dimension information. This helps avoid problems caused by simply marking dimensional tolerances.
a Parallelism Tolerance b Flatness Tolerance c Datum
To summarize, using geometric tolerance can successfully and quickly express what the designer wants, which may not be possible with dimensional tolerance.
Definition in ISO
The connection between size and shape is explained like this:
Specifications in ISO8015-1985 that are shown in blueprints, like size and shape limitations, do not match up with other sizes, limits, or attributes and work on their own unless otherwise specified.
As previously mentioned, the independence principle is a world standard defined by ISO. However, some US companies may not follow the independence principle in accordance with ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) guidelines. To avoid any confusion during trade with foreign companies, it is recommended to negotiate and clarify specification requirements beforehand.
Xiamen Ruicheng offers free consultation for all designs. Feel free to contact us for any production/inspection standards needs .
Post time: Nov-01-2023