Die casting is a metal casting process in which molten metal, typically a non-ferrous alloy such as aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, is injected under high pressure into a reusable steel mold, called a die. The die is designed to form the desired shape of the final product.
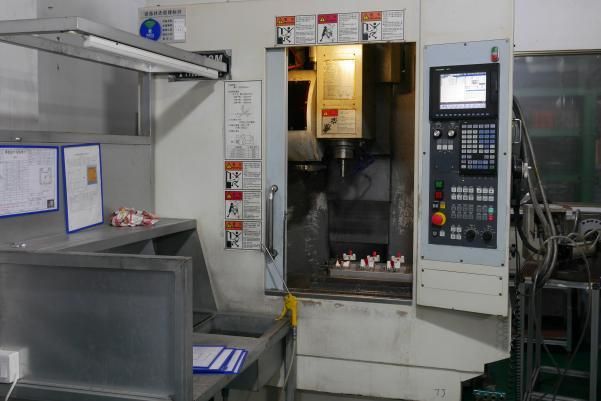


What are the process steps of die casting?
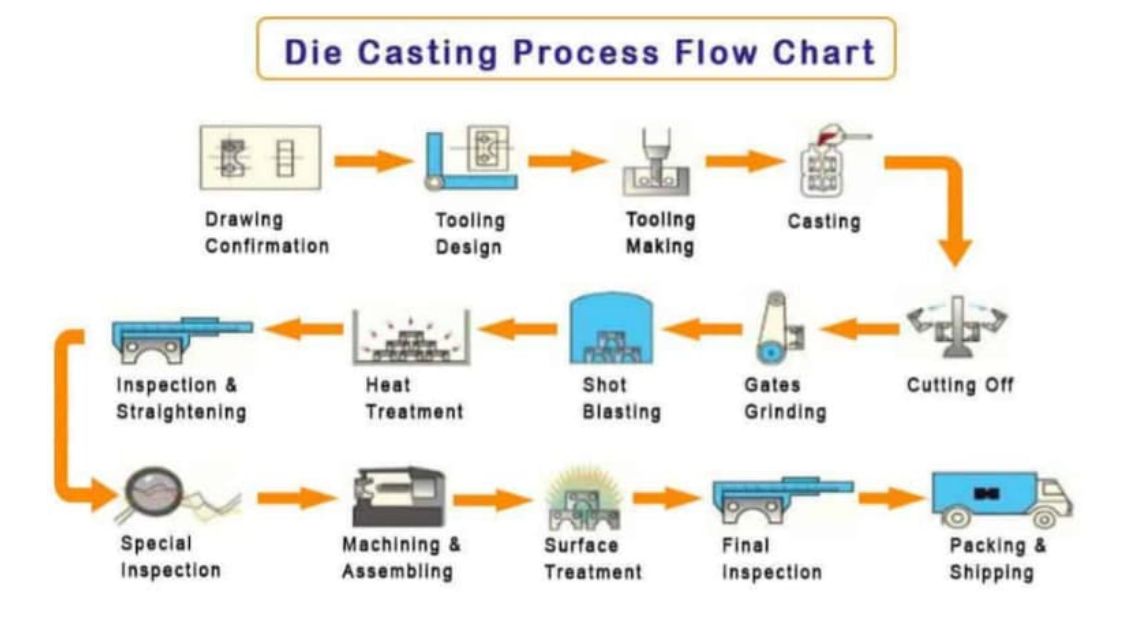
①Die Preparation: The die, also known as the mold, is prepared for the casting process. The die consists of two halves, the fixed half (cover die) and the movable half (ejector die), which create the desired shape of the final product.
②Melting the Metal: The selected non-ferrous metal, such as aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, is melted in a furnace at high temperatures. The molten metal reaches the desired temperature for casting.
③Injection: The molten metal is injected into the die at high pressure. A piston or plunger forces the molten metal into the die cavity through a sprue, runner, and gate system. The pressure helps to fill the mold completely and ensure the desired shape is achieved.
④Solidification: Once the molten metal is injected into the die, it rapidly cools and solidifies within the die cavity. The cooling process is carefully controlled to ensure the metal solidifies uniformly and without defects.
⑤Ejection: After the metal has solidified and cooled sufficiently, the die halves are opened, and the casting, also known as the die casting, is ejected from the die cavity. Ejection pins or ejector plates help push the casting out of the die.
⑥Trimming and Finishing: The ejected die casting may have excess material, known as flash, around its edges. This excess material is trimmed off to achieve the final desired shape. Additional finishing processes such as machining, sanding, or polishing may be performed to refine the surface and dimensional accuracy of the casting.
⑦Post-Treatment: Depending on the specific requirements and application of the die casting, additional post-treatment processes may be carried out. These can include heat treatment, surface coating, painting, or any other required finishing processes to enhance the properties or appearance of the casting.
How to choose the die casting process according to the actual situation?
Choosing the appropriate die casting process depends on several factors and considerations related to the actual situation. Here are some key points to consider when selecting the die casting process:
Material: Identify the type of metal or alloy to be used for the casting. Different metals have distinct properties and characteristics, such as melting temperature, fluidity, and shrinkage rate. Consider the specific requirements of the part or product, such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity, and choose a die casting process that is suitable for the selected material.
Complexity of the Part: Assess the complexity of the part or product to be manufactured. Determine if it has intricate shapes, thin walls, undercuts, or complex internal features. Some die casting processes, such as high-pressure die casting (HPDC) or multi-slide die casting, are better suited for producing complex parts with tight tolerances, while others may be more suitable for simpler designs.
Production Volume: Consider the required production volume. Die casting processes can be categorized into high-pressure die casting (HPDC) for high-volume production and low-pressure die casting (LPDC) or gravity die casting for lower volumes. HPDC is typically more efficient and cost-effective for large-scale production, while LPDC and gravity die casting are better suited for smaller production runs or prototyping.
Surface Finish and Precision: Evaluate the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy requirements of the part. Some die casting processes, such as squeeze casting or vacuum die casting, can provide improved surface finish and tighter tolerances compared to traditional high-pressure die casting. These processes may be preferred for parts that require exceptional surface smoothness or precise dimensions.
Tooling and Equipment: Assess the availability of tooling and equipment required for the die casting process. Some processes may require specialized machinery, such as high-pressure die casting machines or low-pressure casting systems. Consider the cost, lead time, and feasibility of acquiring or modifying the necessary tools and equipment for the chosen process.
Cost and Efficiency: Evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness and efficiency of the die casting process. Consider factors such as material costs, tooling expenses, production cycle time, energy consumption, and labor requirements. Compare the advantages and limitations of different processes to determine the most cost-effective option for the specific production requirements.
Expertise and Experience: Take into account the expertise and experience available in your organization or from die casting suppliers. Some processes may require specialized knowledge, skills, and equipment setup. Assess the capabilities and experience of your team or potential partners to ensure successful implementation of the chosen die casting process.



By carefully considering these factors and consulting with experts in the field, you can make an informed decision and select the most appropriate die casting process for your specific situation.
Welcome to Xiamen Ruicheng such a strong supplier to consult, you will get professional advice!
Post time: Feb-05-2024
