Vacuum casting, also known as silicone molding or polyurethane casting, is a manufacturing process used to create multiple copies of a prototype or part. It is commonly employed in the field of rapid prototyping and low-volume production.
What are the process steps of vacuum casting?
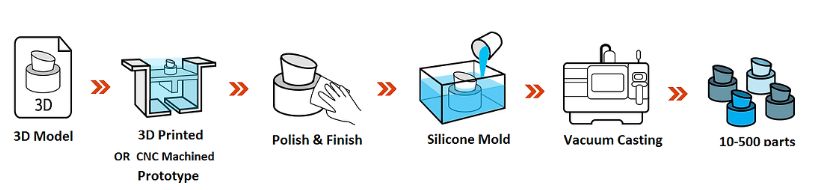
①Master Model Creation: A master model is first produced using 3D printing, CNC machining, or another suitable method. The master model represents the desired shape, form, and details of the final part or product.
②Mold Preparation: A silicone mold is created from the master model. The master model is placed in a container, and liquid silicone is poured over it, covering the model completely. The silicone is then allowed to cure, forming a flexible and durable mold.
③Mold Assembly: Once the silicone mold has cured, it is cut into halves, creating a mold cavity. The halves are then reassembled using alignment features to ensure proper alignment during casting.
④Material Casting: The desired casting material, typically polyurethane resin, is prepared. The mold is preheated to a specific temperature and placed in a vacuum chamber. The vacuum chamber is sealed, and a vacuum is applied to remove any trapped air or gases from the mold.
⑤Pouring and Curing: The prepared casting material is poured into the mold cavity through a small opening or sprue. The vacuum pressure helps to draw the material into the mold, ensuring proper filling and minimizing air bubbles. The mold is then left undisturbed for the material to cure and solidify.
⑥Mold Removal and Finishing: After the casting material has fully cured, the mold is opened, and the replica part is removed. Any excess material or flashing is trimmed and removed. The part may undergo additional post-processing steps, such as sanding, painting, or surface finishing, to achieve the desired aesthetics and functionality.
See What Makes vacuum casting So Popular
Cost-Effectiveness: It eliminates the need for expensive tooling, such as injection molds, which can significantly reduce upfront costs.
Speed and Lead Time:The production cycles are shorter since there is no need for complex tooling or extensive setup.
Speed and Lead Time: Vacuum casting provides relatively fast turnaround times compared to traditional manufacturing processes.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics: Vacuum casting can deliver high-quality surface finishes, replicating the appearance and texture of the desired end product. It produces parts with smooth surfaces, reducing the need for extensive post-processing or finishing.
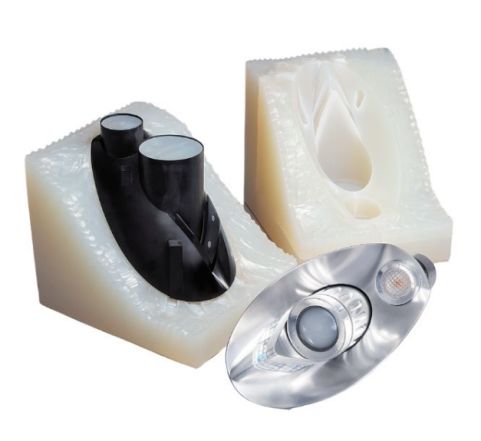


How to choose the vacuum casting process according to the actual situation?
Choosing the right vacuum casting process for your specific situation involves considering several factors. Here are some key considerations to help guide your decision:
Material Requirements: Start by identifying the material properties required for your prototype or product. Consider factors such as hardness, flexibility, transparency, and heat resistance. Vacuum casting supports a wide range of casting materials, including polyurethane (rigid and flexible), silicone rubber, and clear resins. Select a vacuum casting process that can accommodate the desired material options.
Quantity and Production Volume: Determine the quantity of parts you need to produce. Vacuum casting is well-suited for low to medium production volumes. If you require a small batch of prototypes or a limited production run, vacuum casting can be a cost-effective solution compared to other manufacturing methods like injection molding.
Detail Replication and Surface Finish: Assess the level of detail replication and surface finish required for your parts. Vacuum casting is known for its ability to accurately reproduce intricate details, textures, and undercuts. If your design includes fine features or complex geometries, vacuum casting can deliver high-fidelity replicas. Consider the surface finish options available with different vacuum casting processes to ensure they meet your requirements.
Time Constraints: Evaluate your project's timeline and turnaround requirements. Vacuum casting typically offers faster lead times compared to traditional manufacturing processes. Consider the time needed for mold creation, casting, and post-processing. Some service providers may offer expedited services or multiple casting machines, which can reduce lead times. If time is critical, choose a vacuum casting process that can meet your desired timeline.
Cost Considerations: Analyze your budget and cost constraints. Vacuum casting can be a cost-effective solution for low-volume production and prototyping. Compare the costs associated with mold creation, material consumption, and post-processing across different vacuum casting service providers. Be sure to consider the overall value and quality delivered by each option.
Additional Requirements: Take into account any additional requirements specific to your project. For example, if you need overmolding or insert molding capabilities, ensure the selected vacuum casting process supports such features. Consider any specific certifications or standards your parts may need to comply with, such as ISO or FDA requirements.

By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision on the vacuum casting process that is best suited for your specific situation. Additionally, you can consult with our company for vacuum casting services to gain further insight and guidance.
Post time: Dec-04-2023